Epigastric pain , is an upper abdominal pain which can be caused by several diseases. First you need to understand the location of epigastric pain https://andorramed.com/comprar-cialis-generico/. The pain is limited to Epigastrium, it is a part of upper abdomen. Technically it is the region between subcostal plane and costal margins. The image below can help you to understand the location of epigastric pain.
In this article we will discuss causes and general diagnostic and treatment approach for causes of epigastric pain. Each causes are discussed in detail in other articles.
Causes of Epigastric Pain
The epigastric pain can be caused by several diseases. Epigastric region holds many important organs, or parts of important organs like stomach, pancreas, duodenum, abdominal muscles, fascia and peritonuem. Any disease involving these organs can cause epigastric pain. The pain can be non radiating (located to epigastrium) or can radiate to other surrounding areas)
Below are the few most common causes of epigastric pain
Pancreatitis is one of the most common cause of epigastric tenderness or pain, while ulcer disease is also very closely related to epigastric pain but it is seen that most of the Ulcer disease patients do not have epigastric pain. Only less than 20 percent of patients with Ulcer disease complain of epigastric or upper abdominal pain.
It should be noted that diseases like Gastritis, gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers which causes epigastric pain has a close association with local infection from Helicobacter Pylori
Most of the time the cause of epigastric pain remains unknown even after several medical tests and investigation and all the test results come of to be normal, this type of idiopathic epigastric pain is called as Nonulcer Dyspepsia. It is a kind of functional persistent epigastric pain with normal test and investigation results.
Diagnosing Causes of Epigastric Pain
Epigastric pain is a symptom of some underlying disease and the diagnostic approach is to find out the cause and treat it. For diagnosing disease of stomach, barium studies are not that useful. Endoscopy plays an important role, though the invasive nature of the investigation brings the dilemma of as to when to perform it.
Endoscopy is necessary for the diagnosis of cancer and to see changes at the cellular level (Dysplasia) of lower esophagus to rule out Barret's esophagus which could progress to esophageal cancer (adenocarcinoma of esophagus). Even in the case of ulcers, the most definitive test to diagnose it is biopsy and histology which requires endoscopy. So when should a doctor perform endoscopy? well, their are few things to look out for in the history of patients which could be important pointers for performing endoscopy in patients with epigastric pain.
The general rule of thumb is, all patients with epigastric pain should undergo endoscopy except for those whole are below 45 years of age and do not have alarm symptoms like:
There are some other tests which are performed initially in patients with epigastric pain where the doctor suspects an ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori, such as
Treatment of Epigastric pain
Epigastric pain is treated by treating underlying cause. Usually a in patients who have evidence of H.Plori infection can be treated with H2 Blockers, Antacids or PPIs. If this emperical treatment fails, endoscopy should be performed. Also, if their is no evidence of disease like gastritis or ulcer disease there is no point treating for H.Pylori infection. Treatment of all the causes of epigastric pain is discussed in detail in articles for that particular disease
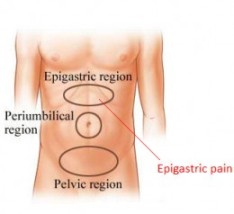 |
Location of Epigastric Pain
Image Source: trialx.com
|
In this article we will discuss causes and general diagnostic and treatment approach for causes of epigastric pain. Each causes are discussed in detail in other articles.
Causes of Epigastric Pain
The epigastric pain can be caused by several diseases. Epigastric region holds many important organs, or parts of important organs like stomach, pancreas, duodenum, abdominal muscles, fascia and peritonuem. Any disease involving these organs can cause epigastric pain. The pain can be non radiating (located to epigastrium) or can radiate to other surrounding areas)
Below are the few most common causes of epigastric pain
- Ulcer Disease
- Pancreatitis
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Gastric Cancer
- Gastritis
Pancreatitis is one of the most common cause of epigastric tenderness or pain, while ulcer disease is also very closely related to epigastric pain but it is seen that most of the Ulcer disease patients do not have epigastric pain. Only less than 20 percent of patients with Ulcer disease complain of epigastric or upper abdominal pain.
It should be noted that diseases like Gastritis, gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers which causes epigastric pain has a close association with local infection from Helicobacter Pylori
Most of the time the cause of epigastric pain remains unknown even after several medical tests and investigation and all the test results come of to be normal, this type of idiopathic epigastric pain is called as Nonulcer Dyspepsia. It is a kind of functional persistent epigastric pain with normal test and investigation results.
Diagnosing Causes of Epigastric Pain
Epigastric pain is a symptom of some underlying disease and the diagnostic approach is to find out the cause and treat it. For diagnosing disease of stomach, barium studies are not that useful. Endoscopy plays an important role, though the invasive nature of the investigation brings the dilemma of as to when to perform it.
Endoscopy is necessary for the diagnosis of cancer and to see changes at the cellular level (Dysplasia) of lower esophagus to rule out Barret's esophagus which could progress to esophageal cancer (adenocarcinoma of esophagus). Even in the case of ulcers, the most definitive test to diagnose it is biopsy and histology which requires endoscopy. So when should a doctor perform endoscopy? well, their are few things to look out for in the history of patients which could be important pointers for performing endoscopy in patients with epigastric pain.
The general rule of thumb is, all patients with epigastric pain should undergo endoscopy except for those whole are below 45 years of age and do not have alarm symptoms like:
- Decrease in appetite
- Weight loss
- Bleeding (heme positive stools)
- Difficulty swallowing or pain while swallowing
There are some other tests which are performed initially in patients with epigastric pain where the doctor suspects an ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori, such as
- H.Pylori serological test
- Stool antigen detection
- Breath testing
Treatment of Epigastric pain
Epigastric pain is treated by treating underlying cause. Usually a in patients who have evidence of H.Plori infection can be treated with H2 Blockers, Antacids or PPIs. If this emperical treatment fails, endoscopy should be performed. Also, if their is no evidence of disease like gastritis or ulcer disease there is no point treating for H.Pylori infection. Treatment of all the causes of epigastric pain is discussed in detail in articles for that particular disease



